Optical illusions have surged in popularity, offering a stimulating brain exercise and a fun way to test your observational skills. These visual puzzles occur when our brains misinterpret what our eyes perceive, leading us to see things that aren't truly there or perceive objects differently than they are. A seemingly still image might appear to move, or identical shapes might seem unequal in size.
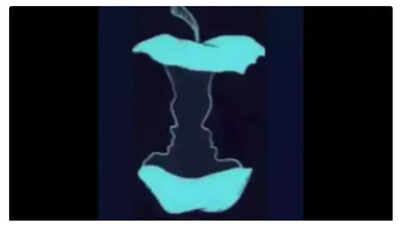
This particular illusion, initially shared by Marina Winberg on social media, presents a classic choice: do you see an eaten apple or two faces? Your initial perception is said to reveal fundamental aspects of your personality. Take a close look and discover what your first glance suggests about you.
Winberg explains, "This image is a classic dual-illusion where you can either see two faces (a man and a woman) looking at each other OR an apple core—what you notice first says a lot about your mindset!"
What does your perception reveal?
Optical illusions fall into three primary categories:
Newer articles
Older articles
 Cervical Cancer: Don't Ignore These 5 Subtle Warning Signs
Cervical Cancer: Don't Ignore These 5 Subtle Warning Signs
 Bezos-Backed Methane-Tracking Satellite Suffers Mission-Ending Failure in Orbit
Bezos-Backed Methane-Tracking Satellite Suffers Mission-Ending Failure in Orbit
 Rishabh Pant's Revolutionary Cricket Reshaping the Game, Says Greg Chappell
Rishabh Pant's Revolutionary Cricket Reshaping the Game, Says Greg Chappell
 Bangladesh Test Captain Najmul Hossain Shanto Resigns After Sri Lanka Defeat
Bangladesh Test Captain Najmul Hossain Shanto Resigns After Sri Lanka Defeat
 Greg Chappell Hails Rishabh Pant's 'Game-Changing' Batting Display Against England
Greg Chappell Hails Rishabh Pant's 'Game-Changing' Batting Display Against England
 Colon Cancer: 5 Subtle Warning Signs You Shouldn't Ignore
Colon Cancer: 5 Subtle Warning Signs You Shouldn't Ignore
 Gujarat Cricket Association Set to Debut T20 League in 2025-26 Season
Gujarat Cricket Association Set to Debut T20 League in 2025-26 Season
 England Captain Stokes Praises Opening Duo After Record-Breaking Chase Against India
England Captain Stokes Praises Opening Duo After Record-Breaking Chase Against India
 'The Traitors' Star Apoorva Mukhija Accuses Sudhanshu Pandey of Abusive Language, Misogyny Following Show's Finale
'The Traitors' Star Apoorva Mukhija Accuses Sudhanshu Pandey of Abusive Language, Misogyny Following Show's Finale
 Bangladesh's Shadman Islam Rallying Behind Teammates After Day 1 Batting Woes vs. Sri Lanka
Bangladesh's Shadman Islam Rallying Behind Teammates After Day 1 Batting Woes vs. Sri Lanka